In maintenance, data integrity refers to the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of the information stored and managed within the maintenance system. It is a critical aspect of ensuring that the data used for decision-making, analysis, and maintenance activities is trustworthy and free from errors or corruption. Data integrity plays a crucial role in maintaining the effectiveness of maintenance processes, supporting asset reliability, and facilitating informed decision-making.
Ensuring data integrity needs a good understanding of which data to record, the data sources and finally how to record and use the data.
How to achieve maintenance data integrity?
There are many elements or webs that together construct the integrity of data. The first of them is the Data accuracy or correctness. Then comes the data consistency and completeness. And, Lastly, Data Reliability.

LOWEST-PRICE-24F-01M

LOWEST-PRICE-24F-01M
Data Accuracy and Correctness:
Accurate data means that the information stored in the maintenance system reflects the true state of assets, work orders, and maintenance activities. Inaccurate data can lead to incorrect decision-making and inefficient maintenance processes. To ensure the quality of the data we can implement data validation checks. This helps to ensure that the maintenance records have only valid and accurate information. This includes validating data formats, ranges, relationships and relevance.
Nowadays, it is hard to analyze data manually. Since decades, we get used to inserting data in spreadsheets to make simple or complex calculations and analysis. So, data collection may be via a digital medium or manual using a pen and a paper checklists. Later on we insert the data collected through either ways in some spreadsheet. That’s a great opportunity to validate that data. The validation is easier in case of a digital medium because the user interface does not accept the data unless it is within the specified format & range. This arises an early alert that something is wrong. In case of Pen-&-Paper, when someone starts to transfer this data to the spreadsheet he/she will start to face same situation.
The acceptable format and range of data is easily set while designing the user interface. For example, this field accepts only whole numbers, no fractions, range is between 20 and 100. Also, we design what happens when a user tries to insert a value violating any of these guides . It can reject the value, it can pop up a warning or, simply mark it with red.

LOWEST-PRICE-24F-01M
How to ensure the collected data relevance and proper relativeness?
Data Relevance means that we are collecting data of the proper equipment and that we recording it in the correct checklist. This is crucial whether this checklist is digital or manual. This can be achieved by cross checking the equipment serial, Name, designation code, barcode or QR code. Also, we need to ensure that we recording data at the proper date and time. So, data recorded today in the second shift is recorded in the checklist of today the second shift not another date or shift.
Data relative correctness means using multiple collected figures and status to cross check the validity of the data. So we can’t record zero current or very low current for an equipment under loading status. Also, we can’t record flow or pressure for a standby pump. Also some figures may defy physical laws as the Pressure and flow at different points of long pipes can’t defy Bernoulli’s principle.
Data consistency and completeness
Data consistency has 2 unfolds; Completeness and Uniformity across the organization. let’s start by the one that is an organizational responsibility; Uniformity across the organization.
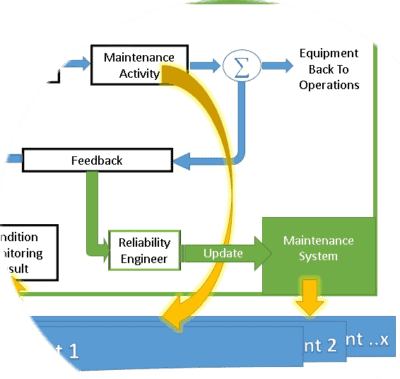
Consistent data ensures that information is uniform across different modules or systems within the maintenance environment. Also, across the organization, any function accessing the maintenance data, should only access the same updated data that is available within the maintenance function. This require the presence of a unified location for data storage and retrieval. We shall talk about securing this data later on in this article. Inconsistencies can arise when data is duplicated, leading to confusion and potential errors. This happens when users take a local copy of the data on their computers at one point of time. Then, later on, they use their version of the data for their analysis not the last version.

LOWEST-PRICE-24F-01M

LOWEST-PRICE-24F-01M
The second aspect of data consistency is the data completeness. Complete data includes all the necessary information required for effective maintenance management. Incomplete data can result in gaps in the understanding of asset history or maintenance activities. Incomplete data might result from unsteadiness of data collection, partial data collection, the wrong collection of data and, data cleansing. All this heavily breach the data integrity.
Data Reliability to ensure data integrity
Reliable data is a trustworthy data and can be depended upon for making critical maintenance decisions. This includes the reliability of equipment data, historical maintenance records, and other information used in the decision-making process. Ensuring Reliability of data comes after ensuring the accuracy, correctness, consistency and completeness. Data Reliability complements all these elements of the data integrity with security, audit, preventing corruption, readability and, integrability.
Security:
Protection Against Unauthorized Access: Data integrity also involves ensuring the security of maintenance data. Unauthorized access or tampering with data can compromise its integrity and lead to potential risks.
Audit
Regular Checks: Conducting periodic data audits involves reviewing and validating data to identify and rectify any inconsistencies, errors, or discrepancies.
Data cleansing : Rectifying any inconsistencies, errors, or discrepancies is essential for maintaining the integrity of datasets, but it requires a thoughtful approach to minimize unintended modifications to data trends. The goal is to enhance data quality without introducing bias or distorting the original characteristics of the dataset.
Tracking Changes: Maintaining audit trails helps track changes made to the data over time. This is crucial for accountability and understanding how data has evolved, preventing unauthorized or unintentional alterations.

LOWEST-PRICE-24F-01M

LOWEST-PRICE-24F-01M
Preventing Data Corruption:
Implementing Safeguards: Putting measures in place to prevent data corruption is essential. This involves implementing safeguards against system failures, ensuring regular backups, and having recovery plans in case of data corruption.
Ensuring System and users Readiness
Training and Documentation: Providing training for personnel who input and manage maintenance data is crucial. Clear documentation of data entry standards and procedures helps maintain consistency and accuracy. It also ensures safe and smooth onboarding of new users.
Integration with Other Systems:
Maintaining Consistency Across Systems: If the maintenance system integrates with other enterprise systems (such as Enterprise Resource Planning or Asset Management systems), ensuring data integrity across these systems is vital for a unified and accurate view of information.
In Conclusion,
Ensuring data integrity in maintenance is fundamental for maximizing the effectiveness of maintenance practices, minimizing downtime, and supporting overall asset reliability. Organizations that prioritize data integrity can make more informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance the overall performance of their maintenance processes.
However there are prior steps to ensuring data integrity. Those steps affects the maintenance process in general, the quality of available data and the possibility to ensure data integrity. Here we mainly mean the good understanding of which data to record, the data sources and finally how to record and use the data.
If you feel you need help with any of these ideas we discussed, request a Management Consultancy or Coaching Services From our Store







One Comment