Every building we construct in our life whether it is a physical or a mental or virtual one has some main elements. There are the foundation which we had covered through the previous couple of posts. Then there are the main skeleton of the construction. The main skeleton houses the different areas of the building and at the center of the skeleton there is the heart. The heart rhythm synchs the operations in all the building areas. At the heart of the maintenance there is the maintenance cycle. The maintenance cycle connects all elements of the maintenance process together. In other words, it links all the sub processes of the maintenance process together.
The maintenance cycle at the heart of the maintenance process pumps the data within the maintenance process. Data to maintenance is like the blood to our bodies we can’t live without either of them.
Our maintenance construction has some essential pillars that come after the foundational pillars of Strategy and People. Those are the Work Management, Material Management, Basic care, Performance management and support systems.
Work Management Pillar i.e. The Maintenance Cycle
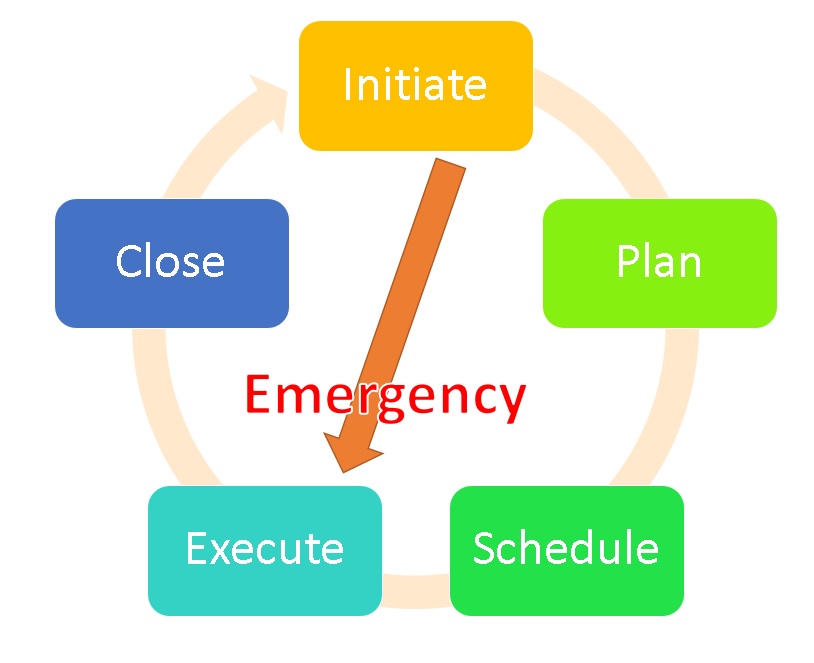
To manage the maintenance work, you need to understand what is the work that you need to do. All the core work of the maintenance is within the maintenance cycle. The maturity of the maintenance cycle means your level in the Work Management Pillar. The Maintenance Cycle starts by the initiation of the maintenance task, then the planning and scheduling efforts. The Emergency condition might bypass the planning and scheduling.
By the way, not every failure is an emergency. So you need to define the emergency conditions that might squeeze the planning and scheduling efforts. Besides, as we explain in our training for building a maintenance program; you can plan your steps in case of an emergency condition well ahead in time. And the zero time of execution can come or not. When it happens, the emergency plan execution occurs. After that we close the task whether it is a scheduled maintenance, a failure or an emergency condition in order to feed the system with data to keep it alive and to initiate a new cycle.
Levels of Maturity within the Work management pillar
As we explained to manage the maintenance work, you need to manage the maintenance cycle. To manage the maintenance cycle, you need to manage the planning and scheduling. So if the heart of the maintenance essentials is the maintenance cycle, then the core of the maintenance cycle are the planning and scheduling. So to grow the maturity of the maintenance cycle we need to grow the maturity of the planning and scheduling. Measuring the performance of the planning and scheduling is a leading key performance indicator that gives an early indication of how the other lagging KPIs will look like.
Level zero, innocence
That’s when there is no planning. Simply there are some maintenance tasks that we want to do. The motivation behind this can be requests from the operators due to deterioration of the equipment performance. Or, it can e simply an inherited habit. Example: we change this bearing every 6 month otherwise it fails and causes more troubles. Scheduling is there if we respond to operators’ request before the equipment totally fails.
Level1, Awareness
We are aware that on stoppage time we can do some tasks together not only the urgent requested one. So, we have a list of the tasks that we shall do during a shutdown. Moreover, most of the shutdowns or at least 50% of them are scheduled and coordinated between the maintenance and operation teams.
Level2, Understanding
Planning takes place early leaving a time for scheduling most of the jobs. Not only that, we all believe in the importance of compliance to the schedules. So, when we measure schedule compliance KPI, we found it is fulfilling our benchmark. SMRP (Society for maintenance and reliability professionals) recommends its benchmark to be >90%. And, it recommends 2 ways to calculate the schedule compliance. One based on the number of executed scheduled works. While the other is based on the hours of scheduled works executed. They look like:
Scheduled Compliance (%) =
(Number of work orders performed as scheduled / Total number of scheduled work orders)
× 100
Schedule Compliance (%) =
[Scheduled Work Performed (hours) / Total Time Available to Schedule (hours)] × 100
Level 3, competence in maintenance cycle
Almost we plan and schedule all jobs. However, we need to grow the maturity of other maintenance pillars to help us achieve this level as we shall see in the coming weeks.
Level 4, excellence
Simply planning and scheduling are standardized i.e. we have a standard procedures for planning and scheduling. We follow those standards and we have plans and schedules ready on the shelf for extended cycles. Then we have time to improve and upgrade the processes.
Explaining the maintenance cycle
Initiate
That’s when a trigger raises a flag that a task will due within the time needed for planning and scheduling. The trigger origin is mainly from the maintenance program. However few requests that work as triggers might come from internal customers in different business units or as a project. This trigger can be activated based on a calendar based scheduled maintenance or the number of operations or operation hours. It also comes from the predictive tasks or measurements that are originally recurring maintenance tasks that reflects the equipment status. Those triggers initiate the planning and scheduling steps of the needed maintenance tasks. As best practice, the predictive maintenance inspector is required to use his human senses besides the tools. It is some sort of visual inspection that the inspector performs along the measurement collection cycles.
Plan
This describes the details of the needed work and how to do it. The plan includes the descriptions and drawings of what has to be done for each job . All materials, tools, subcontractors , etc. are reviewed and secured. Repair manuals are cross checked in case that there is any needed relevant information. The job is not scheduled to start until all the right parts are onsite or at least has a confirmed delivery date.
Schedule
Once materials and team availability have been confirmed , the job can be put on a schedule for execution . Jobs schedules ensure the least disruption to production. Scheduling cycle varies. However, it is best to schedule the job for a weekly cycle , which means identifying next week’s work before the end of this week. But this depends on the needed preparations. We might start planning for some tasks few months or weeks ahead.
The schedule should be revised daily to accommodate emergencies and every effort should be made to complete all work within the week it is scheduled . A successful practice is to allow a portion of the schedule for working on failures in order to minimize schedule disruption . The amount of time allowed for failures will decrease as your proactive maintenance program takes effect and reduces the number of ” emergency ” and ” urgent ” work situations.
Based on the organization policy, the Maintenance supervisors or the planners assign the various teams to the various scheduled jobs. They put together the work details and any additional instructions the supervisor deems appropriate . Unless you are training less experienced workers , use the most appropriately skilled team members rather than whoever is available.
Execute
In successful companies , work crews do the work the right way the first time , and this is where skills , multiskilling , and training pay off . Do not rush the work . If something does not go exactly as planned , correct it . Do not try to work around it just to meet the schedule
Close
When the work is completed , inform operations . If operations is satisfied that the work is indeed ready , the equipment will be deemed ready for production . The parts used , materials used , and other relevant data is recorded on the work order along with any feedback to the planners from the work crews . The work order is closed and the job history data are made available for reliability analysis and standard job plan improvement
In conclusion,
The maintenance cycle links all the maintenance processes together. Improving the maturity of the maintenance cycle will improve the work management pillar. At the core of the maintenance cycle you can find the planning and scheduling. The maturity matrix measures the maturity of the work management pillar through the maturity of the maintenance cycle. We moved from the ground level up to the excellence level and we defined each stage so you can know where you are and how to move forward.
If you feel you need help with any of these ideas we discussed, request a Management Consultancy or Coaching Services From our Store