In the previous chat, we had understood the project initiation and how it resembles the initiation of new maintenance tasks. After initialization i.e. after we documented the need for the task or project, then we need to plan the task or project. The superficial meaning of planning is to put the task in a schedule beside the other maintenance tasks. That’s not what project planning is all about.
The real planning effort has a lot more in it than just scheduling the task. The confusion in the maintenance field occurs when the heart of the planning process is assigned to the maintenance team while the scheduling and coordination were left to the planners. Understanding the project management planning phase can help us understand the true meaning of planning that we need to adopt. It is not important to whom you assign each part of the process, the important is that there are no overlooked steps or sub-processes in the planning process.
The project planning phase
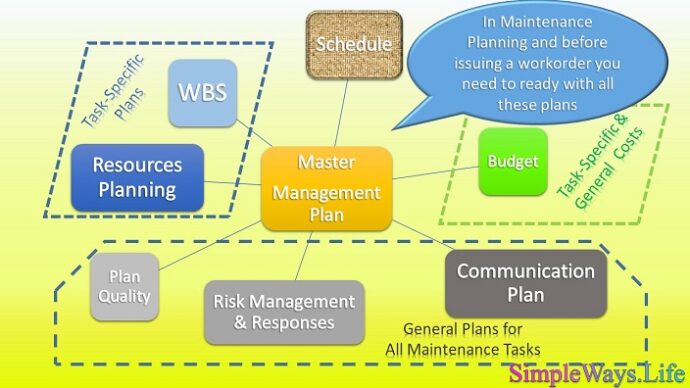
In the project you need to create individual plans then integrate them in a master one. This will create the integrated management plan. That’s the plan around which we manage, execute, control and close the project.
In the planning phase you need to decompose the project into WBS which is the Work Breakdown Structure. WBS decompose the project into smaller, more manageable components by subdividing project deliverables and project work. You continue decomposing till you reach a unit of work that will be executed. Then, you assign team members to execute it and check its interdependencies. Interdependencies might come from the execution team or from another related step. The related step need to be completed or started before this step or after it. That’s part from the resource planning. There is human resource planning and equipment and tools planning.
Schedule and Budget
These individual components allows you to assign time and money to it. Now you are clear what tasks will be in parallel and what must be in series i.e. one task should follow the other. The cost of doing this task is part of your budget. The time and interdependencies will build the schedule.
When you reach a satisfactory WBS i.e. the smallest manageable components, you can decide the procurement, subcontracting and other outsourced activities. Those outsourcing activities feed the budget and schedule.
Plan risk responses
We need first to make a plan for Risk Management. By the way a plan includes the steps to achieve a target. It means to decide on and make arrangements for achieving the target in advance. There is no much difference from planning a family gathering, planning a major maintenance shutdown or planning the International Space Station which is a major global project.
So a Risk Management plan is the plan to achieve the responses in case an anticipated risk occurred. It starts by identifying the risk. Then evaluating it qualitatively i.e. prioritize the risk. Before last, we evaluate the risk effect on the project quantitively i.e. in terms of time and cost. In the last step, we plan countermeasures for risk if it occurred. Before that it is more important from planning responses is to discuss if it is possible mitigate this risk so it wouldn’t occur in the first place.
Communication plan
Since we now understand that the plan encompasses the steps to achieve the target we need to apply this to the communication plan. So to communicate is to send and receive some information or data, what is the difference between information and data? You can find a detailed explanation in our previous article: Intend to make use of the data.
The communication stream runs from the project manager down to the execution level and feedback runs vice versa. However not every piece of information or data need to flow to all levels. Besides, who is accountable for sending this information or reports? Those are the steps that are in the communication plan.
Quality Management Plan
It is important to understand what we mean by quality management or quality plan. It is not the superficial meaning of a having a product with high, good or acceptable quality. The quality management is the overseeing of all activities and tasks to maintain a desired level of output. In simple words, how we can confirm that the all the steps anyone take conforms with the agreed upon procedure or steps.
This includes everything from field execution to report preparation and This includes everything from field execution to report preparation and even the planning process itself. The organization or the workplace has some procedures to follow for doing anything in the workplace. The measurement of the compliance of what is normally or currently executed to how it is planned to be done is the quality management. How to perform this measurement? That’s the quality plan.
Finally,
You end up with a complete master plan of all plans of equipment, resources as manpower, budget, quality, risk response and even communication. The 2 major outputs are the overall schedule with interdependencies and cost of the project. The cost of the project or its budget is strongly related to the execution of each of theses plans.
Project planning lessons that can help maintenance planning
The project planning process group includes a lot of plans and the steps to generate each plan of them.
The first step, the maintenance task details(WBS) and resources
That is the heart of the planning. It is to divide the task or the project to its smallest manageable parts. So, as a part of any maintenance task, we have the resources management. One of the resources can be the tools whether to measure, to test, to dismantle or to lift. Then we consider tools as a whole as a component that we can manage individually. After that comes the team. If it is one team from one discipline, then it is a one component e.g. a team of 4 for 6 hours. That’s of course after defining the skill set they need for this task.
In case members from another discipline are needed then they can be planned separately as they are managed separately and have their own different skill set. You can find an example in repairing the concrete base of an electrical motor. The task needs at least the Electrical team and the construction team and each of them has his own duties within the same activity or task.
Other components of the maintenance task can be the documentation, the safety goggles, spare parts, etc.
Other parts of the maintenance plan
So, the first part of the maintenance task plan was specific to the task. The other parts of the maintenance plan are more general i.e. they govern the maintenance tasks in general. There is a general communication plan within the maintenance team and across teams e.g. between maintenance and production. There should be clearly defined communication points. In other words, who will tell what to whom? Otherwise, there will be random scattered inconsistent information passed throughout the teams working in maintenance. Also, the risk of facing some problems while performing the maintenance task like some parts difficult to dismantle, extra parts need replacement, extra tools, technical advice needed, other problems found during repair and so on.
Who will be in charge of executing the risk response when it occurs to ensure that the equipment is back to operation safely?
Quality Management plan ensures that maintainers follow the the SOPs or the standard operating procedure. Otherwise, it is difficult to tack the root cause of many failures. As maintenance itself if not executed properly, might introduce failures, partial failures or induced failures or even safety accidents or incidents.
Before last comes the cost of maintenance
If we want to calculate the budget of the maintenance, we usually calculate it to the overall maintenance business process over a month or a year. However if we want to control the budget or the spending of the maintenance we need to control it on the level of each maintenance task by optimizing, the parts, time and frequency of the task without jeopardizing the equipment performance.
One of the interesting parts to control is the extra hours cost or the overtime cost. That’s the cost of the manhours we need to complete maintenance activities outside the regular working hours. When there is an organization target to reduce this cost, then the individual tasks performed outside the regular hours are in the focus. Same when we need to reduce spare parts consumptions or outsourcing contracts.
Lastly,
The overall schedule of the maintenance is ready after the coordination and scheduling efforts are completed. Then the workorder for each task carries its shares from the task details and the relevant information from the resources, communication points and , safety procedure by mixing the relevant parts of all the above plans. As you can see some of these plans are specific to the set of tasks that will be executed today and others are general and used as a management plan for the maintenance process as a whole. You can consider the communication plan, the budget and the quality management plan as general governing plans.
In conclusion,
Although maintenance is a recurring task in general, it includes some uncertainty due to the various environmental conditions that affects maintenance. At the same time, maintenance has a major effect on all the business units and the business profitability in general. The processes in the project planning phase are not different from those used in maintenance. However generally , in maintenance and in business, we are not used to use the project acronyms as communication plan and risk mitigation and so on. Understanding the project management principles and resonating to them would add a new expansion dimension to our maintenance process. Today we had made an analogy between the project planning processes and the true complete planning effort needed for maintenance. This analogy is an eye opening to what we should include in the true complete maintenance plan.
If you feel you need help with any of these ideas we discussed, request a Management Consultancy or Coaching Services From our Store





3 Comments